
Parts of a Flower and Plant and Their Functions (8 Diagrams Flower
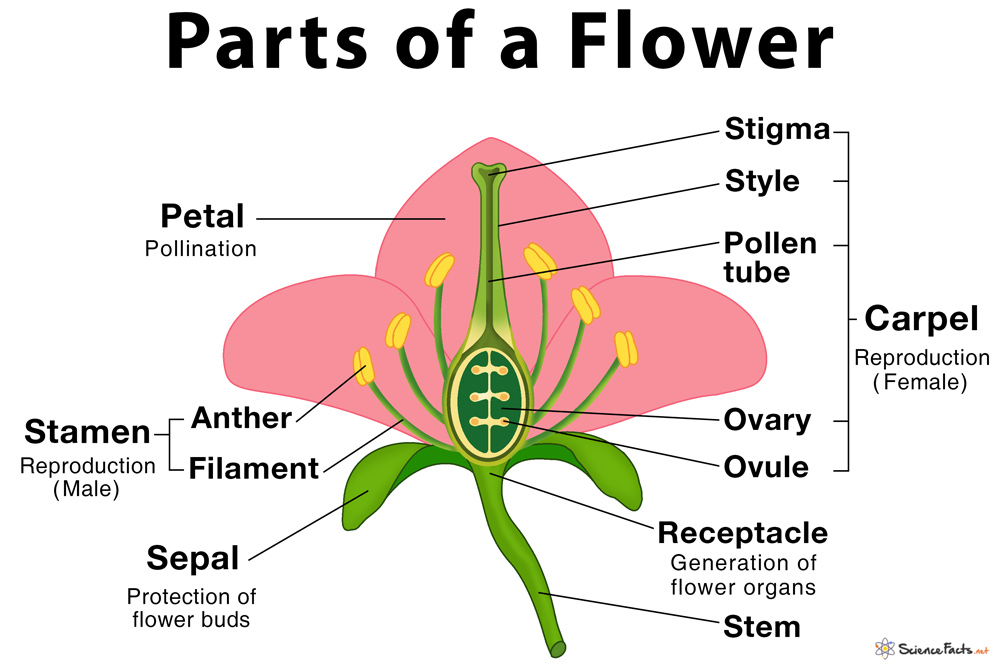
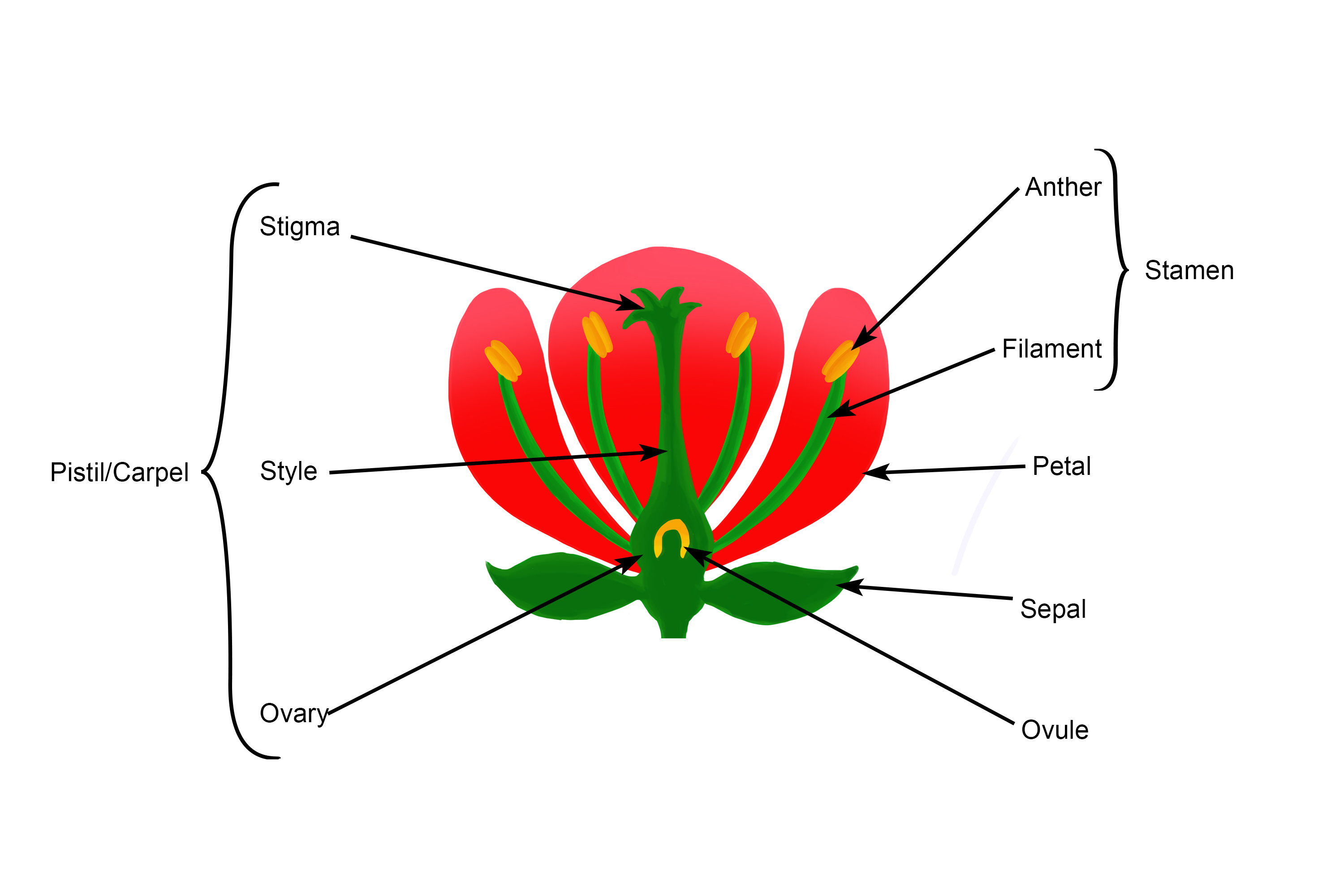
When looking at a diagram of a flower, the ovary is the enlarged part located at the base of the pistil. The function of the ovary is to protect its ovules that fertilize pollen that reaches down the pollen tube. One of the reasons why flowers are necessary for fruit-bearing plants is for fruit to form properly. Once fertilized, the ovary.
Parts of a Flower, Their Structure and Functions With Diagram
Flower Structure in a Labelled Diagram. Flower structures are complex, so just knowing the names of each one might not solve all your questions. To get a better idea of what each part of a flower looks like, have a look at the labelled diagram below. Fig. 1 - Diagram of a complete flower showing the four main floral parts and their components.
3a1 Flowers Nature Journals
A typical diagram of a flower is divided into four main parts: 1) sepals, 2) petals, 3) stamen and, 4) carpel, each of them performing distinct functions. When a flower has all the four floral parts, it is called a complete flower. A flower missing any one of them is called an incomplete flower. Parts of a Flower Diagram. 1. Sepals.

The Life Cycle Of A Flower Discover How Flowering Plants Reproduce
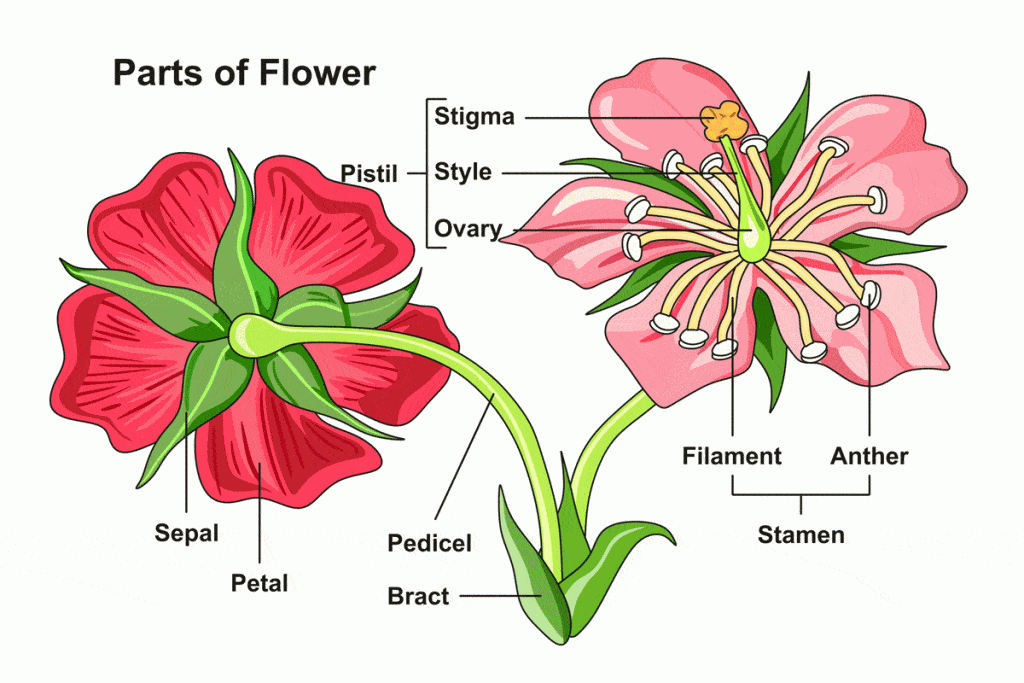
In a flower diagram, stamen are located on both sides of the pistil. The stamen consists of two parts: Anther: The anther is the head of the stamen. It produces pollen. Filament: The filament is the stalk attached to the flower that holds the anther. The stamen's function is to produce male reproductive cells.
A typical flower and its parts Online Science Notes
Selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram. Flowers are how most plants produce seeds. In this interactive, you can label the flower parts. Use your mouse or finger to hover over a box to highlight the flower part to be named. Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the main parts of the flower.

Parts of a Flower and Their Functions (With Diagram) (2023)
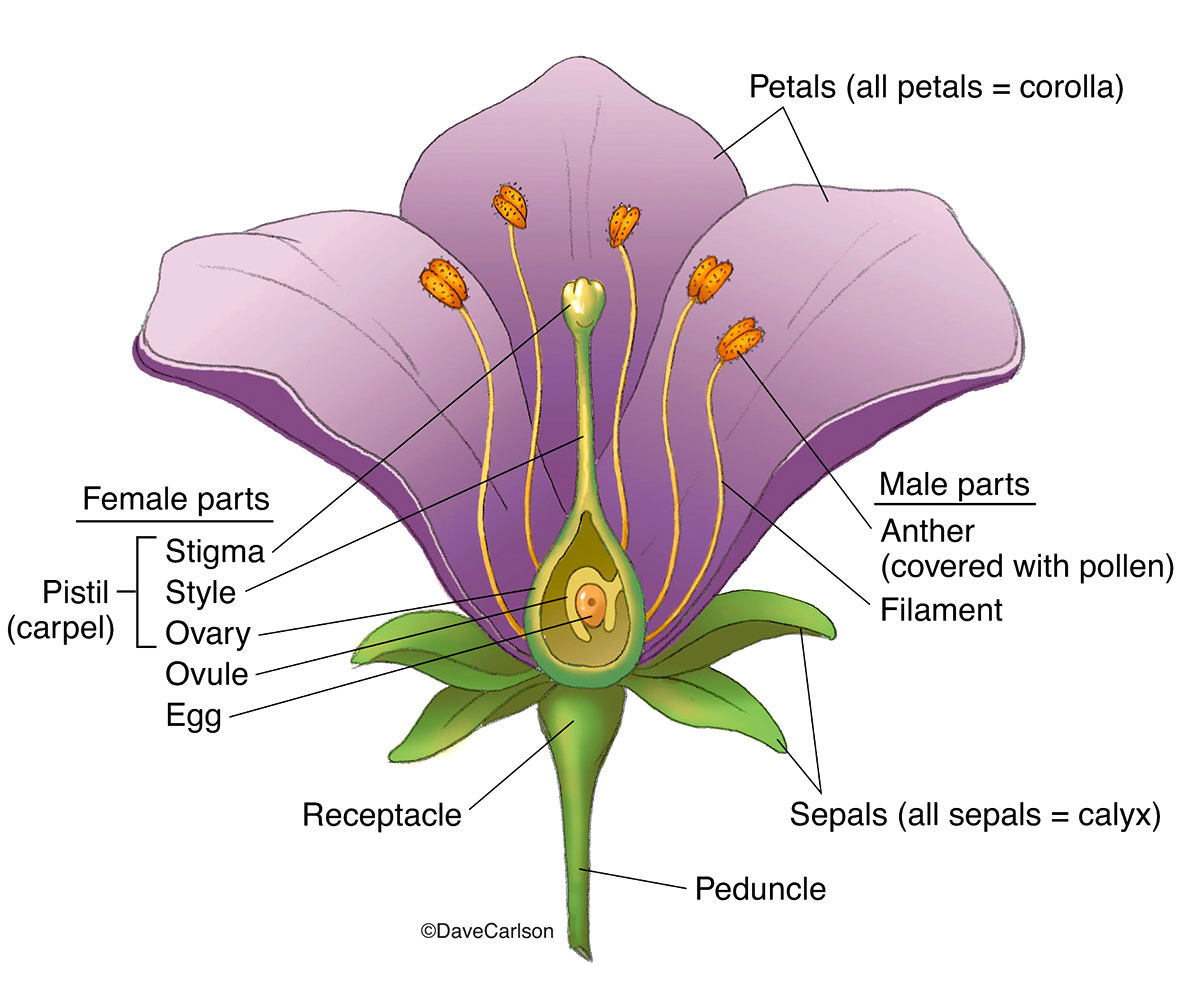
The Four Main Flower Parts. Sepals: the protective, leaf-like outer parts of a flower.; Petals: the often colorful structures that attract pollinating animals to the flower.; Stamens: the male parts of a flower.Each stamen consists of a stalk called a filament and a pollen-producing tip called an anther. The stamens of many flowers are designed to shed pollen onto a pollinating animal such as.

Parts of a Flower — Mathwizurd
Printable Flower Diagrams. Using printable diagrams is a great way to teach and become familiar with all the parts of a flower. To download either the labeled diagram above or unlabeled printable diagram below, click on either the diagram itself or the caption. It will open using Adobe Reader. From here you will be able to either save the.
What Are The Parts Of A Rose Plant?
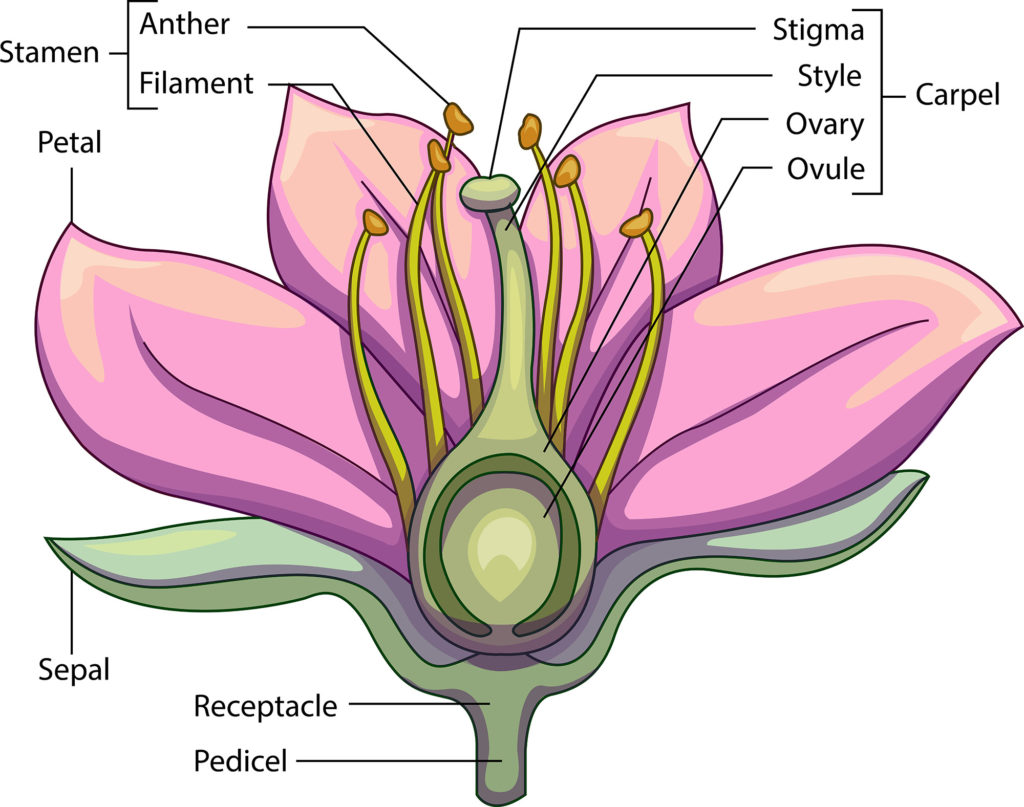
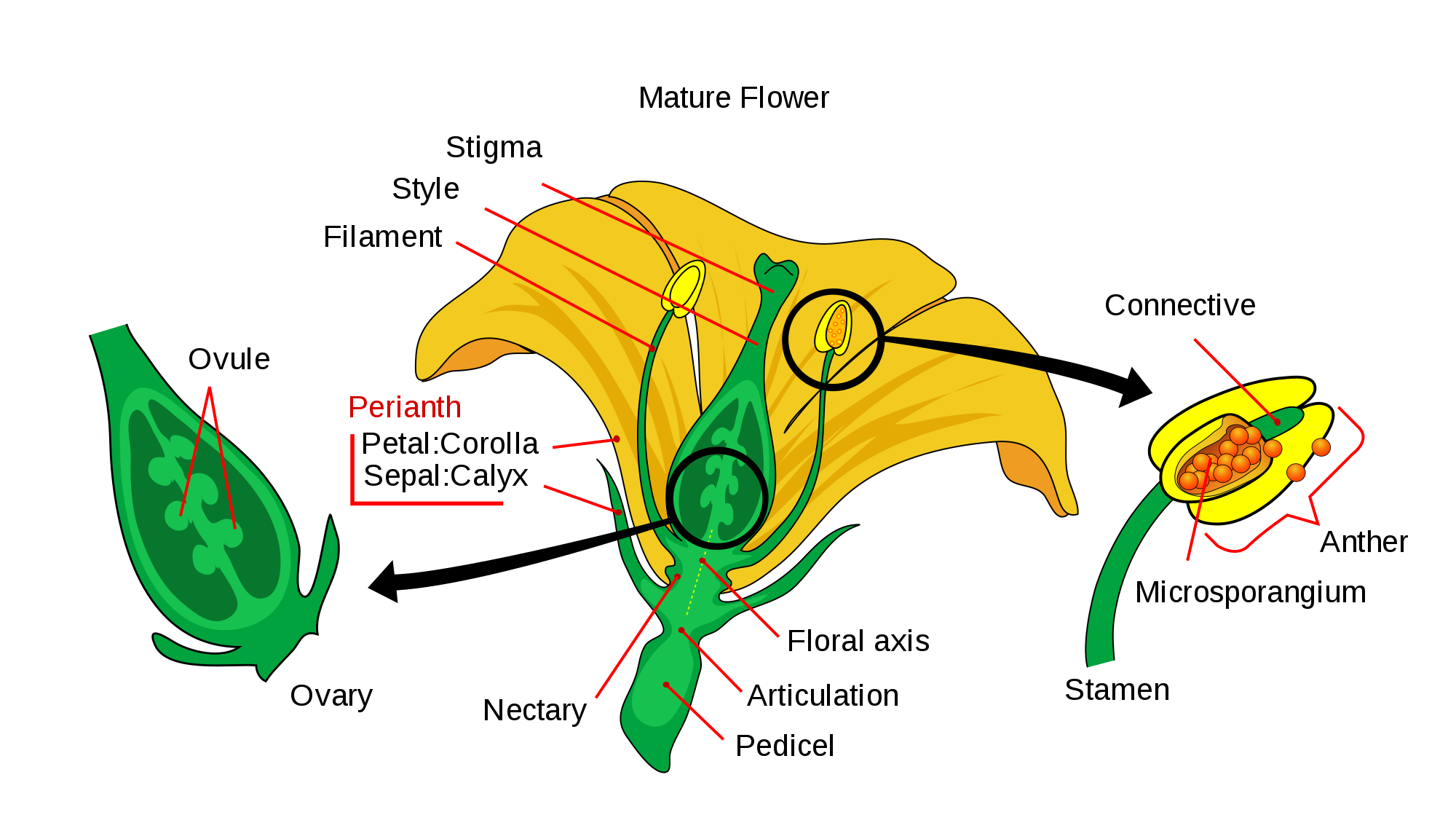
There are commonly four distinct whorls of flower parts: (1) an outer calyx consisting of sepals; within it lies (2) the corolla, consisting of petals; (3) the androecium, or group of stamens; and in the centre is (4) the gynoecium, consisting of the pistils. pistil and stamens. A lily flower with a central pistil surrounded by stamens.
Flower structure diagram / RHS Campaign for School Gardening
A typical flower has four main parts or whorls referred to as the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. The outermost whorl of the flower has green, leafy structures known as sepals. The sepals, collectively called the calyx, help to protect the unopened bud. The second whorl is comprised of petals, usually, brightly colored and are.

Flower Structure Biology for Majors II
GO. Flowers are the reproductive organs of a plant and contain male and female parts. Sepals, petals, stamens and carpels form the four main parts of a flower. The stamens form the androecium, the male reproductive part, and the carpels form the gynoecium, the female reproductive part.
Hibiscus Flower Male And Female Parts Unit 6 Plant Form and Function
Stamen - The male part of the flower that serves to produce pollen; it is composed of the pollen-bearing anther and the stalk-like filament. Pistil - The female part of the flower that typically consists of the stigma at the top which receives the pollen, the narrow style, and the ovary which contains ovules that will later develop into seeds.

Education The Sructure and the Function of Flower
Vegetative Parts of a Flower (Perianth) Petals (Corolla): Petals are usually the most noticeable part of a flower and serve a vital function in attracting pollinators. The vibrant colors and enticing scents of petals attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds. Sepals (Calyx): These are small, modified leaves that enclose and.
Male And Female Parts Of A Flower And Their Functions All Categories
Some flowers have all four of these basic structures. We call these complete flowers.Examples of plants with complete flowers include lilies and roses. Flowers missing one or more of the flower parts are called incomplete.Some, like dogwood, have both pistils and stamens but are missing sepals or petals; these are called perfect flowers.Other plant species separate the male and female.
Parts of Flowering Plants
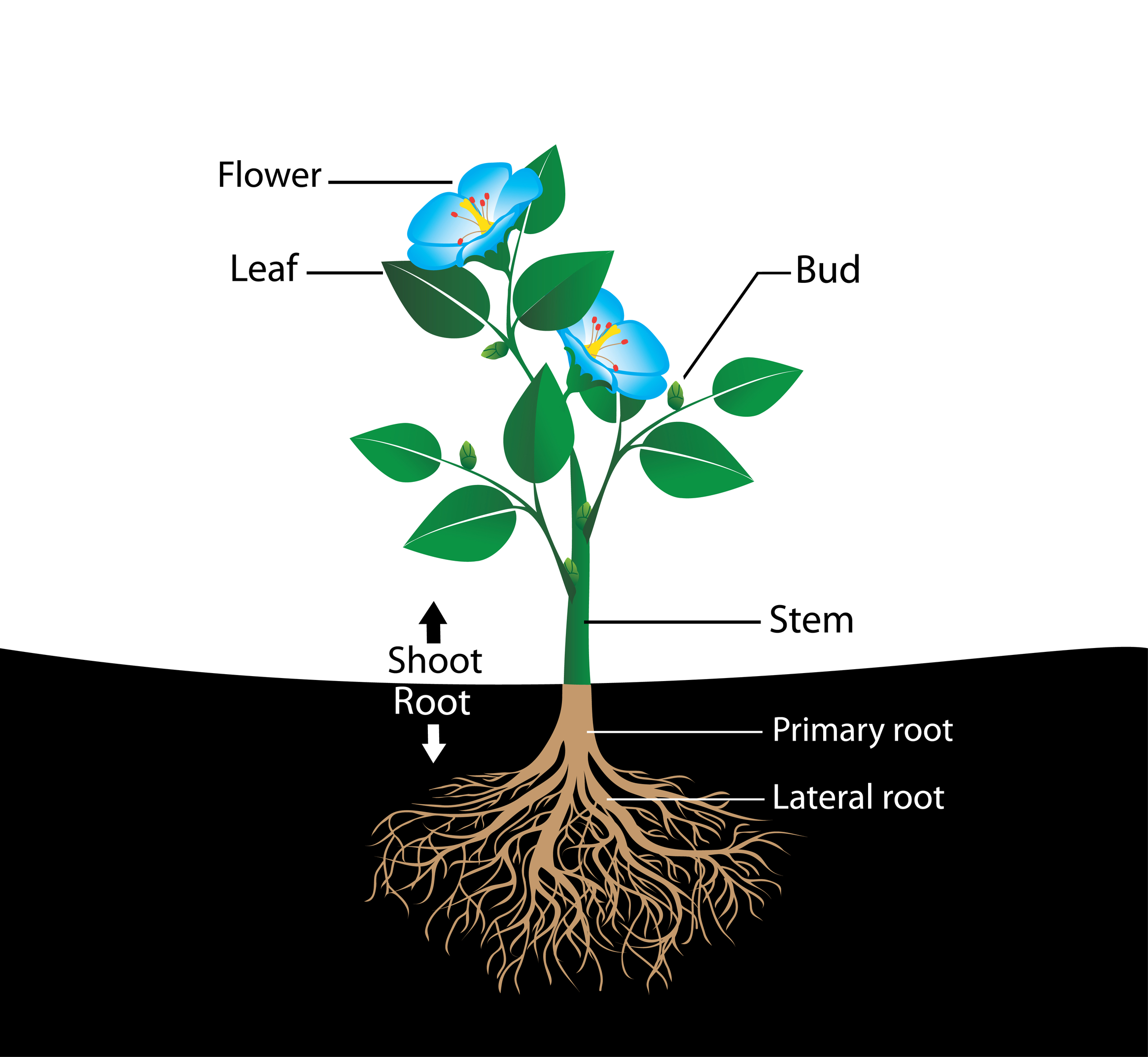
A complete flower consists of two different parts: Vegetative Part; Reproductive Part; Also read: Flowers and Inflorescence. Let us have a detailed look at the different parts of a flower. Flower - L abelled Diagram. Below is a well labelled and simple diagram of a flower for your better understanding.

Monocot vs Dicot Flower Definition, Structure, 6 Differences, Examples
Prep: Before you present this lesson, become familiar with the anatomy of a flower by researching and viewing diagrams or images online or at the library. Teachers TalkingScience recommends that you hand out to your students printed copies of a diagram of the parts of a flower's anatomy that are explored in this activity. Or you can draw a.

The Flower Flower Bouquet, Parts, Functions, Classification of Flowers
In the diagram of the flower below, add labels for all of the bolded terms above and assign each whorl a different color. Make a key for the colors and whorls. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Floral Structure. Symmetry and Quantity. Two other features used to identify flowers are symmetry and the number of parts in each whorl.